Week 8: Nanotech+Art
Nanotechnology has been around for decades. But C60, a soccerball-like structure was actually inspired by the study of extraterrestrial space where people picked up chemical signals of its shape. It was called geodesic domes due to the 60s hippie influence ("Nanotech Jim pt2"). It is interesting how artistic movements leave traces in the evolution of nanotechnology.
Ancient Roman pottery also utilized nanoparticles. Lycurgus Cup found in 400 B.C. has gold colorization because Roman people found a way to incorporate nan-scale gold particles into the creation of pottery, one of the earliest examples of using nanotechnology to create artistic values ("Nanotech Jim pt3").
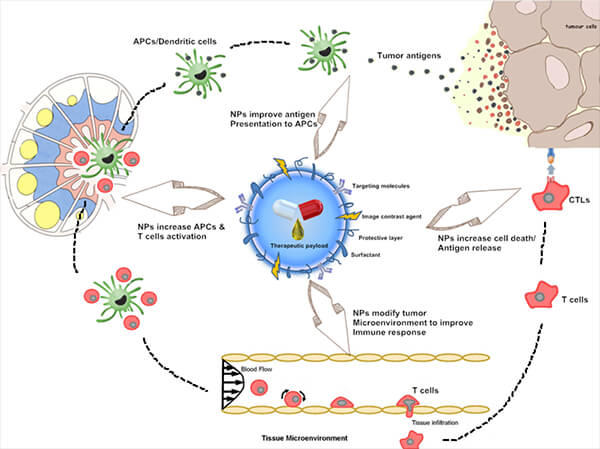
Nanoparticles not only play parts in commercialized products but also in saving lives. Nanotechnologies have been researched to target and eliminate tumor cells. How they work is that they are small enough to enter the blood-brain barrier and heat up when hit by near-infrared light, effectively killing targeted cells ("Nanotech Jim pt4"). "Disease and nanostructures are very closely related," concludes Dr. Gimzewski, after he demonstrates the signaling of cancerous cervical cells through abnormality in filamentary structures ("Nanotech Jim pt5").
Christa Sommerer and Laurent Mignonneau, creators of Nano-Scape, aim to enhance accessibility to the nano-world by utilizing touch. Their innovative approach involves a wireless magnetic force-feedback interface that enables users to interact with invisible nanoparticles: this interaction results in the formation of a dynamic invisible sculpture, constantly changing its shape and properties as users engage with it and with one another (“Art in the Age of Nanotechnology”).
Image/Video citations:
Sources:
Gimzewski, Jim. “Nanotech Jim pt2”. Bruin Media Reserve, uploaded by UC Online, https://bruinlearn.ucla.edu/courses/160989/pages/unit-8-view?module_item_id=5946347
Gimzewski, Jim. “Nanotech Jim pt3”. Bruin Media Reserve, uploaded by UC Online, https://bruinlearn.ucla.edu/courses/160989/pages/unit-8-view?module_item_id=5946347
Gimzewski, Jim. “Nanotech Jim pt4”. Bruin Media Reserve, uploaded by UC Online, https://bruinlearn.ucla.edu/courses/160989/pages/unit-8-view?module_item_id=5946347
Gimzewski, Jim. “Nanotech Jim pt5”. Bruin Media Reserve, uploaded by UC Online, https://bruinlearn.ucla.edu/courses/160989/pages/unit-8-view?module_item_id=5946347
“Art in the Age of Nanotechnology.” Art.Base, art.base.co/event/2104-art-in-the-age-of-nanotechnology#9. Accessed 26 May 2023.

/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/phenomenon-Glow-With-Flow-631.jpg)
Hello!
ReplyDeleteI was also fascinated by the use of nanoparticles in ancient works. Although I was intrigued by how they used the particles for a cup, I also found it interesting that the same particles could be found in window artworks, such as those in older churches. I also enjoyed reading about Nano-Scape from you! I did not realize that there was something invented that would allow users to interact with invisible nanoparticles by utilizing touch. How do users engage with one another with it?